Challenges and Threats of Domain Impersonation
Cybercriminals use domain impersonation to steal money or sensitive data — and this tactic is on the rise. Add that to the resource constraints many organizations face, and it becomes clear why these attacks are difficult to detect and stop.
The two most common forms of domain impersonation are look-alike domains and email spoofing.
Look-alike domains are nearly identical to legitimate ones but slightly altered to deceive users, often used to harvest credentials or distribute malware.
Email spoofing is a widespread tactic in phishing and spam attacks, where cybercriminals forge a sender’s email address without needing to register a domain—making it quick, easy, and highly effective.
Domain Impersonation Protection Products
DMARC Protection for Email Authentication
Another effective way to fight impersonation is by implementing DMARC reject on your email domains. When attackers misuse your domain to send malicious emails, they can deceive your customers and cause lasting harm to your brand reputation and trust.
DMARC is a vital email authentication protocol that empowers administrators to block hackers from exploiting domains for email spoofing, executive impersonation, and spear phishing. However, email systems are complex, so configuring DMARC correctly is crucial to ensure only fraudulent emails are blocked without disrupting legitimate communication.

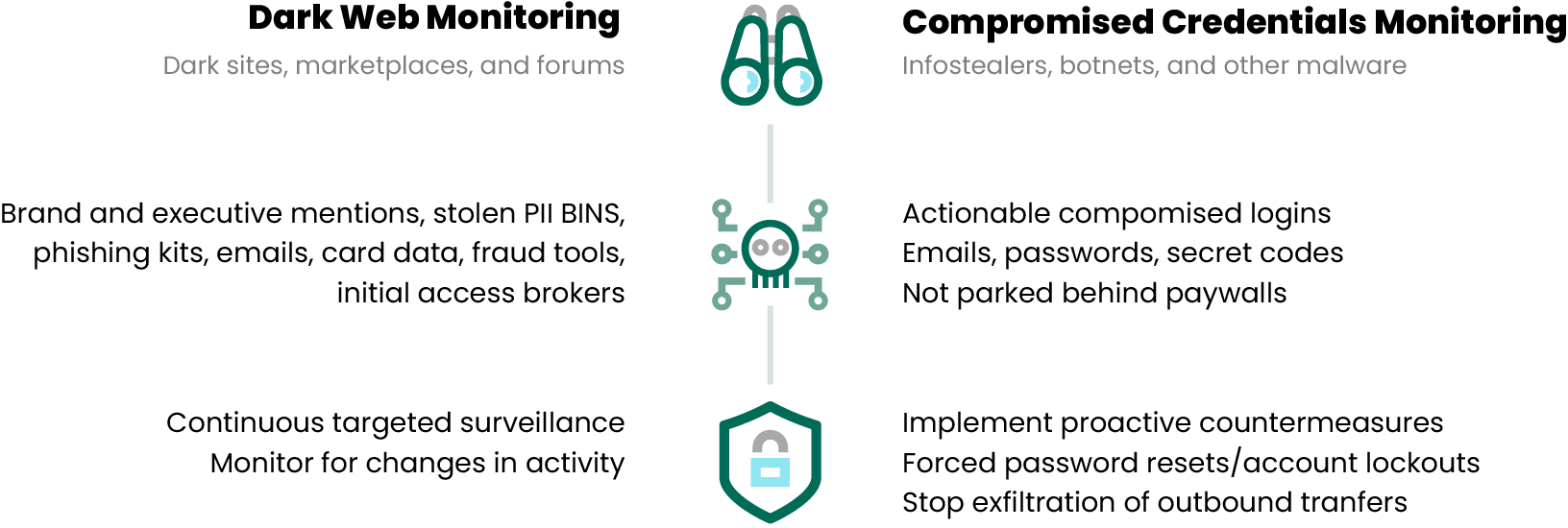
Domain Monitoring
Organizations should also prioritize protecting their domains from threats like look-alike domains. Domains are critical assets frequently targeted by cybercriminals aiming for financial gain through deceptive, similar-looking domains.
Due to limited resources, tackling look-alike domains can be a daunting task for organizations acting alone. That’s why solutions that gather and analyze threat data while enabling rapid takedown actions are essential. Combining domain monitoring with DMARC protection provides a powerful defense against these impersonation threats.
Stop Domain Impersonation
Domain protection should be a core element of any organization’s cybersecurity strategy. Yet, the effort required to safeguard domains and subdomains often exceeds what most teams can handle internally. Effective domain security involves a comprehensive service that covers detection, analysis, mitigation, and continuous monitoring of domains for:
- Domains that contain brands or identified terms
- Being used in a “malicious” manner where the purpose is used to steal customer data, alter customer transactions, or exhibits other properties indicative of fraudulent activity
- Being used in an “unauthorized” manner
Another part of combatting domain impersonation involves implementing DMARC reject on email domains. When a cybercriminal uses a domain for email threats, they can mislead an organization’s customers causing long-term damage to the organization’s brand and customer trust. Fortra DMARC Protection is an email authentication protocol that enables administrators to prevent hackers from hijacking domains for email spoofing, executive impersonation, and spear phishing.
Finally, removing malicious domains is essential for effective protection against impersonation. Fortra accelerates takedowns by swiftly acting on domains involved in phishing attacks, helping to reduce the time and cost organizations spend on monitoring and managing defensive measures.
