Domain impersonation is a tactic used by cybercriminals where fake email addresses or website domains are created based off valid organizations. The impersonated assets are used to trick individuals for money or sensitive data. According to Fortra’s 2023 Domain Impersonation Report, of look-alike domain threat types, 54% hosted brand content, 37% redirected to a third-party site, and 10% hosted malicious content.
The two common types of domain impersonation are look-alike domains and email spoofing.
Look-alike domains
Look-alike domains are deceptive web addresses that closely resemble legitimate ones, often with subtle changes. These nearly identical or confusingly similar domains are intentionally registered to mislead users — commonly for phishing, fraud, or brand impersonation. Attackers use various techniques to create them, including misspellings, character substitutions, added words, or alternate domain extensions.
For example, with use of internationalized domain name (IDN)/homoglyph domains, a popular domain can be altered with a character or two to look similar but obviously not the same: arnazon.com or amazön.com.
Once a look-alike domain is registered, DNS A records are created. The cybercriminal can then create a website and an SSL certificate. Now the website is ready for distribution. This can lead to phishing attacks, malware, and various scams as well as a tarnished reputation and loss of trust for the legitimate organization. While all of this can happen quickly, sometimes the cybercriminals may wait on the look-alike domain to obtain a better trust score. Just because a look-alike domain isn’t in plain sight, doesn’t mean it isn’t lurking for future use.
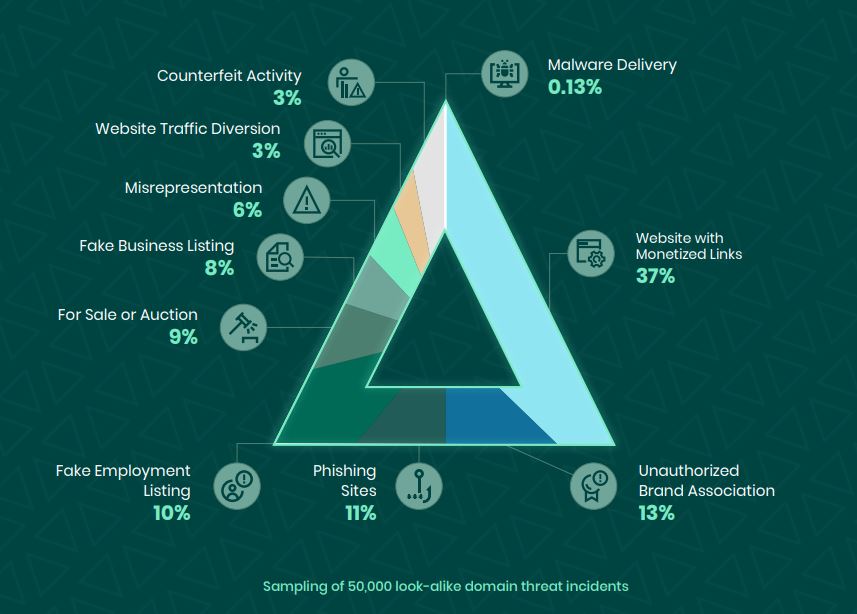
Domain impersonation can take many forms, including monetized links, adult content, unauthorized brand associations, phishing for credentials, and counterfeit operations.
Email spoofing
Email spoofing is a common cybercrime tactic that involves identity deception and is widely used in phishing and spam attacks. It underpins the mechanism required to conduct hacking activities, and it can take many forms. Unfortunately, most email users will eventually receive an email that has been spoofed — whether they know it or not.
Email spoofing does not require a registered domain as it is a forgery of an email sender address. Once a look-alike domain is registered, MX DNS records are created for mail. This can lead to a setup of a mail server and the cybercriminals can send emails.
Display name deception is often successful because email clients usually show only the display name. Cybercriminals can insert the identity of a trusted individual or trusted brand into the display name. This type of attack is simple and cheap to stage.
In addition to manipulating the display name, cybercriminals may also use the actual email address of the impersonated identity in the From header, such as “United Customer Service” . This type of attack, known as a domain spoofing attack, does not require compromising the account or the servers of the impersonated identity, but exploits the security holes in the underlying email protocols. They often use public cloud infrastructure or third-party email sending services that do not verify domain ownership to send such attacks.
Do Domain Impersonations Work?
These impersonation schemes are gaining traction. Fortra’s Domain Impersonation Report also reported that the average brand is targeted by 40 look-alike domains per month.
Fortra took a sample from intel based on 50,000 incidents across all industries and found the following information.
Common Challenges
Many organizations face significant resource challenges that make combating domain impersonation difficult. Following are some of the most common obstacles impacting the majority of businesses.
Lack of visibility
Insufficient intelligence across digital channels caused by an absence of resources brings a lack of visibility needed to identify domain abuse. It is nearly impossible for organizations to monitor everything on their own because of the number of registrars to manage (contacts, procedures, relationships, etc.).
Too much noise
The volume of data can be overwhelming, making it difficult to accurately detect domain threats. Most organizations lack the refined curation and their submitted abuse reports may be ignored.
Ineffective mitigation
Slow, costly, and often unsuccessful, mitigations can be near impossible for organizations to do on their own. A lack of a procedural playbook for each registrar and an overwhelming number of relationships to maintain are just some of the reasons mitigations and proper takedowns are usually unsuccessful.
Limited resources
If the previous challenges do not deter organizations from mitigations on their own, the results might be just enough. Underestimating time, staff, and budget often leads to mediocre results due to insufficient resources.
What Can Organizations Do to Protect Themselves from Domain Impersonation?
Organizations can leverage a domain monitoring service, which encompasses detection, analysis, mitigation, and ongoing monitoring of domains for the following:
- Domains that contain brands or identified terms
- Being used in a malicious manner where the purpose is to steal customer data, alter customer transactions, or exhibits other properties indicative of fraudulent activity
- Being used in an unauthorized manner
What Is Needed for Successful Domain Monitoring?
The following steps are essential for effective domain monitoring.
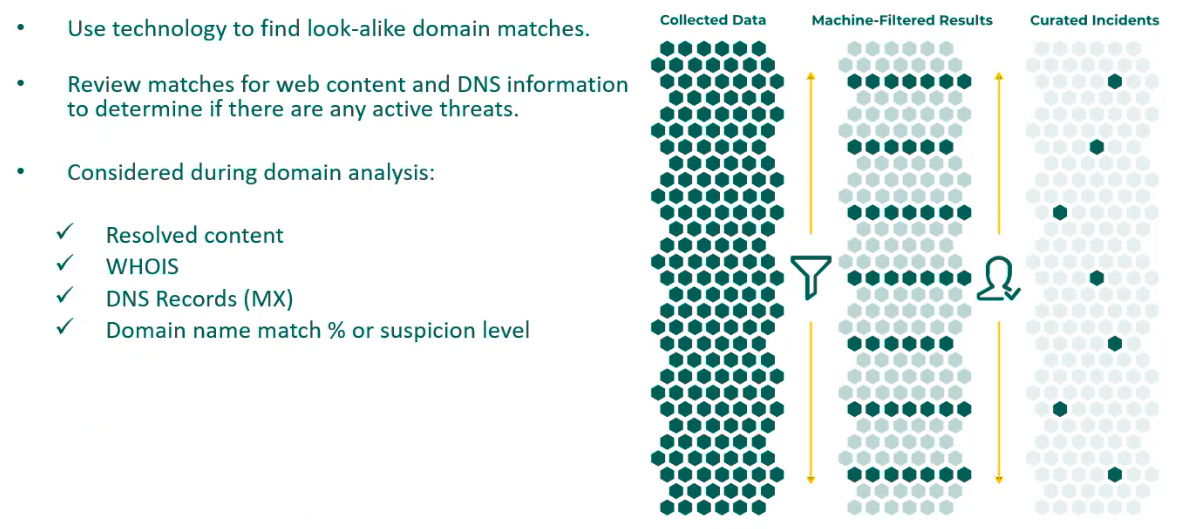
Collection of domain data
- Use DNS zone files and/or third-party domain services to review newly registered domains
- Use SSL transparency logs to find new SSL certificate registrations that contain key terms
- Active DNS: Generate DNS queries to see if a domain exists
- Passive DNS: Monitor DNS traffic to learn about new names
- Client Submission and Client Intelligence
Curation
- Review new gTLDs and ccTLDs
- Search new SSL cert registrations for key terms
- Identify typo-squatting and/or imposter domains
- Monitor domains for changes to website content, MX records and WHOIS data
Mitigation
- Legitimate abuses lead to takedown or suspension
- Internal security tools block malicious domains
- Brand infringement can be mitigated or monitored
The takedown of malicious domains is fundamental for successful protection against impersonation. Having a cybersecurity solution that streamlines takedowns will reduce corporate spend on defensive efforts monitoring/managing registrations.
DMARC Protection for Email Authentication
Another way to combat impersonation is to implement DMARC reject on your email domains. When a cybercriminal uses your domain for email threats, this can mislead an organization’s customers causing long-term damage to the organization’s brand and customer trust. DMARC is an essential email authentication protocol that enables administrators to prevent hackers from hijacking domains for email spoofing, executive impersonation, and spear phishing. But email is complicated and getting email authentication correct is critical, so that only the spoofing is blocked.
Protecting against email spoofing is essential, and strong email authentication is typically effective at detecting spoofed messages. Email authentication standards, such as DMARC, can be used by a domain owner to prevent spoofing of their domain.
A Complete Domain Protection Strategy
Fortra provides solutions to stop domain impersonation and email spoofing. With some of the fastest takedowns in the industry and superior DMARC, organizations can be confident that we will break the attack chain.