This is a Tripwire guest blog.
Despite increasing data breaches, ransomware attacks, and assorted cyber threats, convincing the Board of Directors to invest in robust cybersecurity isn't always easy for many businesses. The challenge originates mainly from the need to demonstrate a quantifiable return on investment (ROI) from any cybersecurity initiative. Many Boards concentrate on performance indicators, profits, and strategic resource distribution, while cybersecurity primarily focuses on risk mitigation.
It is crucial to bridge this communication gap to ensure the board understands and acknowledges the significance and value of cybersecurity.
Decoding the Language of the Board
To clearly convey the value and ROI of cybersecurity initiatives, it's essential to speak the Board’s language, one focused on business growth, risk mitigation, and strategic investment.
Here are some key points to consider:
Return on investment
A constant concern for Board members is the ROI of any proposed investment. They demand clear insights into the concrete and abstract advantages the company will gain in relation to its investments. This is a reasonable expectation. Cybersecurity’s value often lies in preventing costly disruptions rather than generating direct revenue, making its ROI harder to quantify in traditional terms.
Solutions like privileged access management (PAM) and secure remote desktop protocol (RDP) can offer a quantifiable ROI by maximizing resources when it comes to securing access to applications and systems.
The ROI from PAM can come in several forms. First, there are direct cost savings from preventing security breaches. According to a recent report, the average cost of a data breach in 2025 is $4.44 million. By investing in a PAM solution, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of experiencing these breaches, which usually far outweighs the cost of implementing the solution.
Beyond direct cost savings, PAM delivers indirect ROI by helping organizations meet regulatory requirements. By managing privileged access to critical systems, businesses can avoid costly legal penalties and ensure ongoing compliance.
Business risk management
Board members have a deep understanding of risk factors. They acknowledge risks can't always be entirely eliminated but can be supervised and minimized. In discussions about cybersecurity, underline how the proposed investment will help mitigate the risk of cyber events and the ensuing financial losses.
This approach needs to be unique and tailored to the specific organization and clearly identifies the risks that are most relevant to the organization. This could include risks related to a specific vulnerability in remote access systems or risks posed by expanding IT infrastructures.
Information presented to board members must use accurately collected data, such as statistics and case studies to demonstrate the potential impact of these risks on the organization. After identifying and prioritizing risks, present the PAM solution as a critical tool for mitigating them.
Cost analysis
Board members often rely on cost analysis to weigh a project's expected benefits against its inherent costs. In cybersecurity, those benefits typically include safeguarding the company’s reputation, avoiding regulatory penalties, and protecting critical business data.
Strategic value over time
Board members favor initiatives that offer enduring strategic progress. In terms of cybersecurity, this entails maintaining customer trust, ensuring seamless business operations, and securing a competitive edge in the industry.
5 Hidden Costs of Ineffective Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is often seen as a cost center rather than an investment, but this perspective can be misleading. An insufficient cybersecurity strategy can lead to hidden costs that far outweigh the initial investment in robust security measures. Following are examples of potential hidden costs:
1. Financial loss from data breaches
The most obvious cost comes from data breaches. Depending on the sensitivity of compromised information, whether from a profit and loss spreadsheet or a complex business database, a company can incur costly extortion demands from cyber criminals, financial compensation for affected customers, and regulatory fines.
For instance, T-Mobile's 2021 breach compromised over 53 million customers' data, leading to around $350 million in fines and legal costs. Beyond this, the intangible loss of customer trust and reputation can have long-lasting financial impacts on the company.
2. Damage to brand reputation
A security breach involving sensitive data can have serious consequences for a company, damaging its standing in the public eye and affecting customer confidence and loyalty. Although it is challenging to quantify the precise repercussions, incidents like these can have a lasting effect on a company's economic health. Rebuilding a damaged reputation is a lengthy and resource-intensive process, further escalating the overall expenses.
LastPass, a password management company, faced a serious setback when it experienced a security breach. This incident led to the exposure of customer email addresses and password hashes. Given the nature of their business, this breach significantly impacted their reputation for reliability and security.
3. Operational disruptions
Cyber-attacks can disrupt business operations, leading to downtime and loss of productivity. The cost of these disruptions can escalate quickly, especially for businesses that heavily rely on digital operations.
For instance, businesses offering online services like e-commerce platforms or cloud-based applications can experience significant repercussions if there's a breach of their clients' data. Since these services typically operate on a subscription model and cater to a wide customer base, any operational disruptions can result in numerous missed revenue opportunities.
4. Legal expenses
Organizations may face lawsuits from affected customers or partners in a data breach. These legal proceedings can be costly in terms of monetary expenses and the time and resources required to manage them.
Frequently, lawsuits stemming from data breaches escalate into class-action cases, potentially resulting in substantial legal settlements and fines. These costs are an added burden following a cyber-attack, further damaging a company's reputation and standing if held responsible for the breach. The widespread attention these lawsuits attract also can erode customer confidence.
5. Increased insurance premiums
After a major cyber incident, businesses often face rising insurance premiums, an often-overlooked cost that compounds over time. When added to legal fees, reputational damage, and lost business opportunities, these hidden expenses can significantly erode the bottom line.
Evaluating Cybersecurity's ROI
Determining the ROI for cybersecurity can be complex due to its many intangible aspects.
In contrast to other investments, cybersecurity doesn't typically yield direct revenue. Instead, it is a protective shield, protecting revenue and safeguarding the company's assets. As such, the ROI for cybersecurity is often computed based on the cost savings from potential threats that were averted due to the security measures in place.
Here's a fundamental approach to assessing the ROI on cybersecurity:
- Identify Possible Losses: Identify what your organization will lose if targeted by a cyberattack. This includes direct costs such as system recovery and legal expenses and indirect consequences like brand damage and loss of customer trust.
- Estimate the Likelihood of a Cyberattack: While precise predictions are difficult, historical data and industry trends can provide insights into the likelihood of your business being targeted by a cyberattack.
- Calculate Potential Cost Savings: Multiply the evaluated risks of a cyberattack by its estimated likelihood to estimate the potential savings from specific cybersecurity measures.
- Deduct the Cost of Cybersecurity Measures: Lastly, subtract the cost of your cybersecurity efforts from the estimated savings to find the ROI.
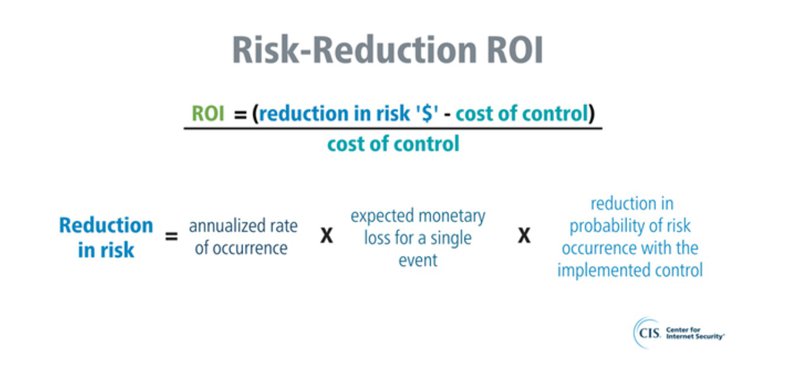
Image Source: CIS
How to Get Your Board on Board with Cybersecurity
Clear communication with your board is critical to securing cybersecurity investments. By framing ROI in terms that resonate with board members and presenting it with clarity and impact, you increase the likelihood that your cybersecurity priorities receive the focus and funding they deserve.